Splunk – ServiceNow
This CMDM product is developed end of 2020 by Eduard Lekanne from The Dutch Data Difference. This product is typical for how The Dutch Data Difference is different: namely being innovative and making functional solutions and/or integrations.
The first use case of the CMDM has to focus on ServiceNow CSDM/CMDB/CMS and Splunk. Problems that this product in the context of ServiceNow and Splunk addresses are:
- Remove the need for shadow CMDB’s in Splunk (tags, lookups, etc)
- Build Splunk Dashboards, Reports, Alerts based on proper CMDB content and/or context (e.g. give me all servers (hosts) for application X)
- Functional integration between ServiceNow CMDB, Incident, Problem, Changes, Users, and Groups.
- All mentioned ServiceNow content now also available in context.
- Powered by a graph database that acts as a cache close to the Splunk environment (low latency) for fast answers
- Improves adoption of ServiceNow IPC and CMDB
Splunk host-based tags
Have you ever closely looked into a Splunk Enterprise environment that is used for Operations? If so you will recognize the use of hundreds if not thousands of host-based tags. And what I mean with host-based tags is that people are defining this host (server) is for “production” or for this “application”. Yes, we know tags from Cloud, Container, or microservices where they are attached as part of the code, but here they are defined manually by some engineer. And of course, the biggest problem here is the maintenance of these. Being a Splunk admin for some time I was often confronted with the question of why a certain dashboard was not presenting the latest or correct information. Often that had to do with not updated tags and other times with having hosts (servers) hard-coded into those dashboards.
The solution is to populate Splunk knowledge objects (Dashboards, Reports, Alerts, etc) dynamically based on updated CMDB data. That way once the CMDB is updated all Splunk knowledge objects are using the same updated information.
Splunk CMDB data into indices
I have seen organisations using the “Splunk add-on for ServiceNow” and also teams onboarding it that way in their “own” index. The latest is even worse as CMDB data is inserted multiple times into Splunk.
Although Splunk is optimized for searching in normal event indices (time-based) the problem is that to know the status of a certain CI one has to search way back in time. And the other problem is how to find the relations between all those CI’s also in relation to Incident, Problem, and Changes.
The solution is to use a new search command “gsearch” with what you can query the CMDB content and context. The underlying graph database ensures fast response to questions related to the state of an object or questions about relations. With another new search command “gpath” one can automatically keep Splunk IT Service Intelligence Services and Entities up-to-date.
Solution: Ready for ServiceNow
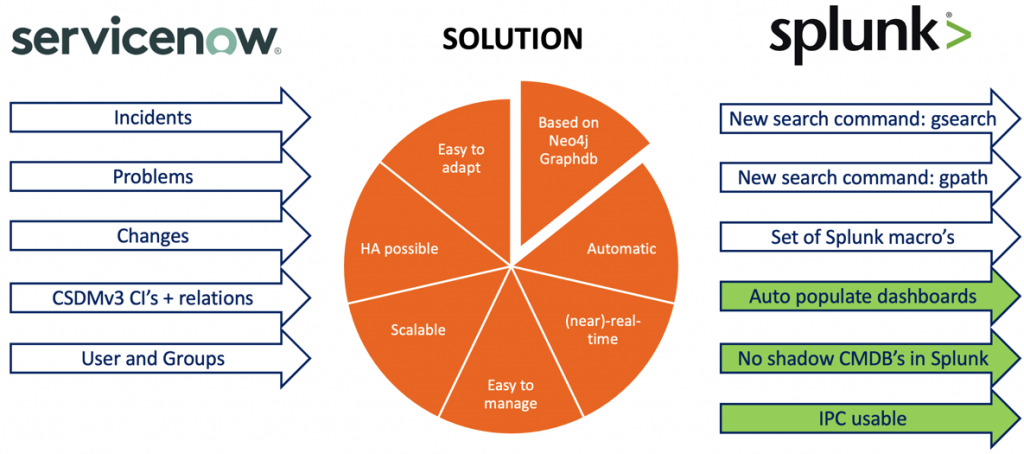
In the above picture one can see:
- On the left, all ServiceNow records that are input into the solution. The CSDM includes CMDB and includes CI’s as well as non-CI’s.
- The solution is in the middle and consists of: graph database, scripts, and Splunk search commands. For now, we offer this solution only on-premise but we are working on getting this offered as a service.
- On the right, from within Splunk users can make use of new search commands and/or pre-defined search macro’s. The arrows in green are showing what they deliver.
Examples
Example 1: query CMDB information.
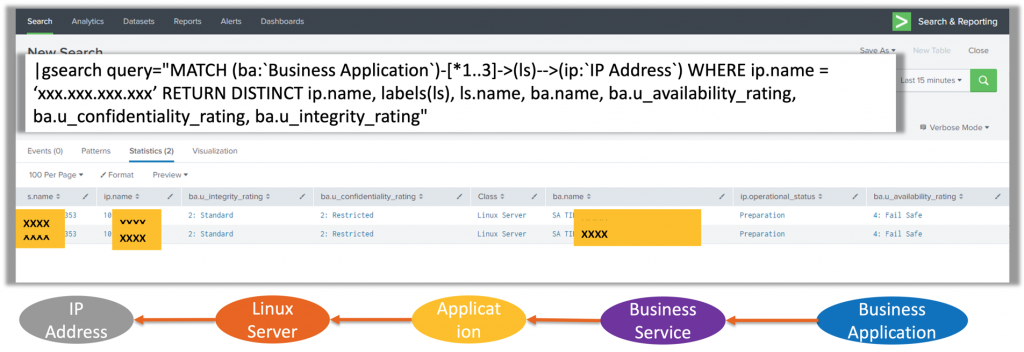
In the above screenshot one can see the “gsearch” command into action. At the bottom of the screenshot one can see the traversal of CI’s that are within the CMDB and that needs to be traversed to give the answer. In this case the answer is the name of the server, the Business Application this server is related to and the Availability, Integrity, and Confidentiality (AIC) rating for that Business Application. Special note here is that CMDB’s are not always that structural so the depth of the relationships is not always the same.
The value of this that Splunk now can also be used based on CMDB content and context. The result is at least less shadow CMDB’s within Splunk and also improved adoption of ServiceNow CMDB.
Example 2: dashboard showing open Incidents, Problem, and Changes for the ITIL Groups the Splunk logged user is belonging to.
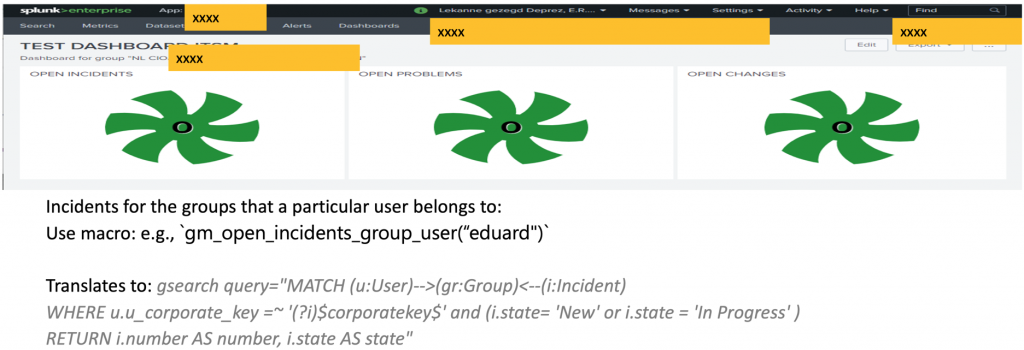
This dashboard shows the open Incidents, Changes, and Problems for the ServiceNow ITIL Groups this Splunk logged in user belongs to. To achieve this the dashboard is populated with three Splunk macro’s. Everytime this dashboard is refreshed the macros will fetch the latest information from the graph database.
This can be achieved by looking into ServiceNow itself but most of the DevOps teams have their operational dashboards in Splunk so it makes sense to present it there. If they want to interact with such an Incident, Problem, or Change they do that within ServiceNow directly.
Installation and setup
For now, the product is only available for on-premise installation close and into a Splunk Enterprise environment. For that, a Neo4j graph database needs to be installed and configured. And the current version of the product supports out-of-the-box only ServiceNow CMDB/CSDM.
Recent Comments